Micromobility is here to stay, and it’s changing how we experience urban life for the better. With Unagi’s membership program, you can enjoy all the benefits of a top-tier electric scooter without the sky-high price of ownership or the inconvenience of ride-sharing.
While e-scooters have been gaining popularity due to their convenience and relatively low cost, they have been getting more attention lately for another reason: battery fires.
It's important to understand the potential dangers associated with the battery technology that lies at their core. Most electric scooter batteries contain highly flammable materials, so they could ignite if exposed to the wrong conditions - making it essential that we understand how electric scooter batteries work, why such scooter fires occur, and their common causes.
Thankfully, these events are not particularly common; however, arming ourselves with this knowledge is a surefire way to guarantee our safety as we enjoy the unique experience of riding these e-scooters.
How to Prevent Electric Scooter Battery Fires
Safety is always a priority when working with lithium batteries, as they can potentially start a fire if not handled properly. Luckily, there are some easy steps you can take to reduce the chances of a lithium battery fire. These Include:
General Practises
- First and foremost, Don’t use counterfeit li-on batteries. Counterfeit batteries are often made with substandard materials that may not meet safety standards and can easily fail during battery operation. These batteries can also lack safety features such as battery management systems and temperature control circuits, which are necessary for protecting against unsafe levels of charge and discharge current that could lead to thermal runaway reactions. It's crucial to ensure that your scooter's lithium-ion battery has been thoroughly tested and meets safety standards set by UL or FCC.
- Keep your devices clean- Dust, and dirt can build up on the battery contacts and cause them to overheat. Be sure to clean your e-scooter regularly with a soft, dry cloth.
- Don’t disassemble or puncture your battery. It's important to handle your battery carefully and avoid dropping it or subjecting it to other forms of physical damage.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to extreme heat or cold. Most of these li-ion batteries have a safe operating temperature between 4°F to 140°F (-20°C to 60°C, respectively). Going out of range could cause not just a decrease in performance but also the risk of the battery failing and even catching fire.
- Inspect for battery damage regularly. Before using your lithium-ion battery, inspect it for any damage, such as cracks, dents, or leaks in the battery casing. If you notice any damage, do not use the battery; instead, replace it with a new one. This may however be tricky if the battery is inbuilt into the electric scooter as they are usually inaccessible. However, if you notice even minor disturbances like loose wiring or strange sounds when the scooter is in operation, consider taking it to a specialist.
- Use a battery case or fireproof bag when transporting battery packs.
Charging Practises
- Don’t use damaged chargers or unauthorised chargers. Make sure you use a charger specifically designed for your electric scooter and that it is in good condition. Avoid using generic or third-party chargers, as they may be unsafe and could result in overcharging or over-discharging of the battery, which could lead to a fire.
- Don’t overcharge your device. Leaving your device plugged in for extended periods can also increase the risk of a battery fire. Only charge your battery when it is low and unplug it as soon as it reaches full capacity. Thankfully, most electric scooter batteries have a Battery Management System that will stop the charging process automatically once the battery is fully charged, but we should still be extra cautious and not rely on that alone.
- Always read and follow the manufacturer's instructions regarding charging and use of the battery - this includes paying attention to maximum charge levels and temperature thresholds.
Storage Practises
- If you are not using the battery, make sure to disconnect it from the electric scooter if possible.
- Store the lithium-ion batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Temperature is critical! Even though 15°C - 20°C (room temperature) is the ideal temperature range for storage of most li-ion batteries, it's important to double-check the manufacturer's temperature recommendation since this isn't always the same across all brands. Typically, temperatures higher than 50°C or lower than -5°C can damage your battery, reduce its life span, or worse, increase the risk of fire or explosion.
- Battery should be stored in dry areas. Humid environments can be detrimental to e-scooter battery cells, as it can lead to the corrosion of the terminals and even create a short circuit.
- Keep them away from metal objects such as coins, keys, or jewelry. Why? This is because metal objects can conduct electricity, and if any of these items come into contact with the battery's terminals, a short circuit could occur, which can lead to a fire.
Lastly, keep an eye on recalled battery cells from time to time; manufacturers may issue recalls due to defects and other safety concerns that may have arisen. If there is a recall for the type of battery you are using, be sure to read the instructions accompanying the recall carefully; often, there may be specific steps you need to take to secure a replacement or get a refund on a faulty battery.
What Type of Battery Do Most Electric Scooters Use?
Lithium-ion batteries are the clear winner when it comes to powering electric scooters. With their high energy densities, lightweight and compact designs, they offer the perfect combination of specs for electric scooters, which are often limited by space and need to be light enough to carry.
Yes, lead-acid batteries may still be around in some capacity, but they offer inferior performance as they use a sort of outdated technology. Furthermore, they are heavier and larger than lithium-ion batteries, which has made them less common now.
Apart from that, lithium-ion batteries are also the preferred choice for most scooter manufacturers due to the following reasons:
- High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries have higher energy density(100-265 Wh/kg), which means they can produce more power with less weight as compared to lead-acid batteries, which typically have an energy density of 30-50 Wh/kg.
- Lithium-ion rechargeable batteries require very little maintenance and have a greater lifespan.
- Lithium-ion batteries are more efficient. They are nearly 100% efficient, which means they can turn almost the entire charge into usable power. On the other hand, lead acid batteries have an efficiency of 85%.
- They have a lower charging time compared to lead-acid batteries.
- They have a lower self-discharge rate. This means that a li-ion battery pack can stand idle for longer stretches without significantly losing charge.
Lead acid batteries, on the other hand, offer a much lower upfront price point than their li-ion counterparts. This is why companies like Razor still rely on them to provide cost-efficient solutions for consumers. However, when it comes down to deciding between a slight price difference or raw performance, many are likely to take the latter approach, which is why lithium-ion batteries are preferred.
Now that we know that lithium-ion batteries power most electric scooters, let's delve deeper into their inner workings to understand better what could potentially cause them to fail and result in fire hazards.
How do Lithium-ion Batteries Work?
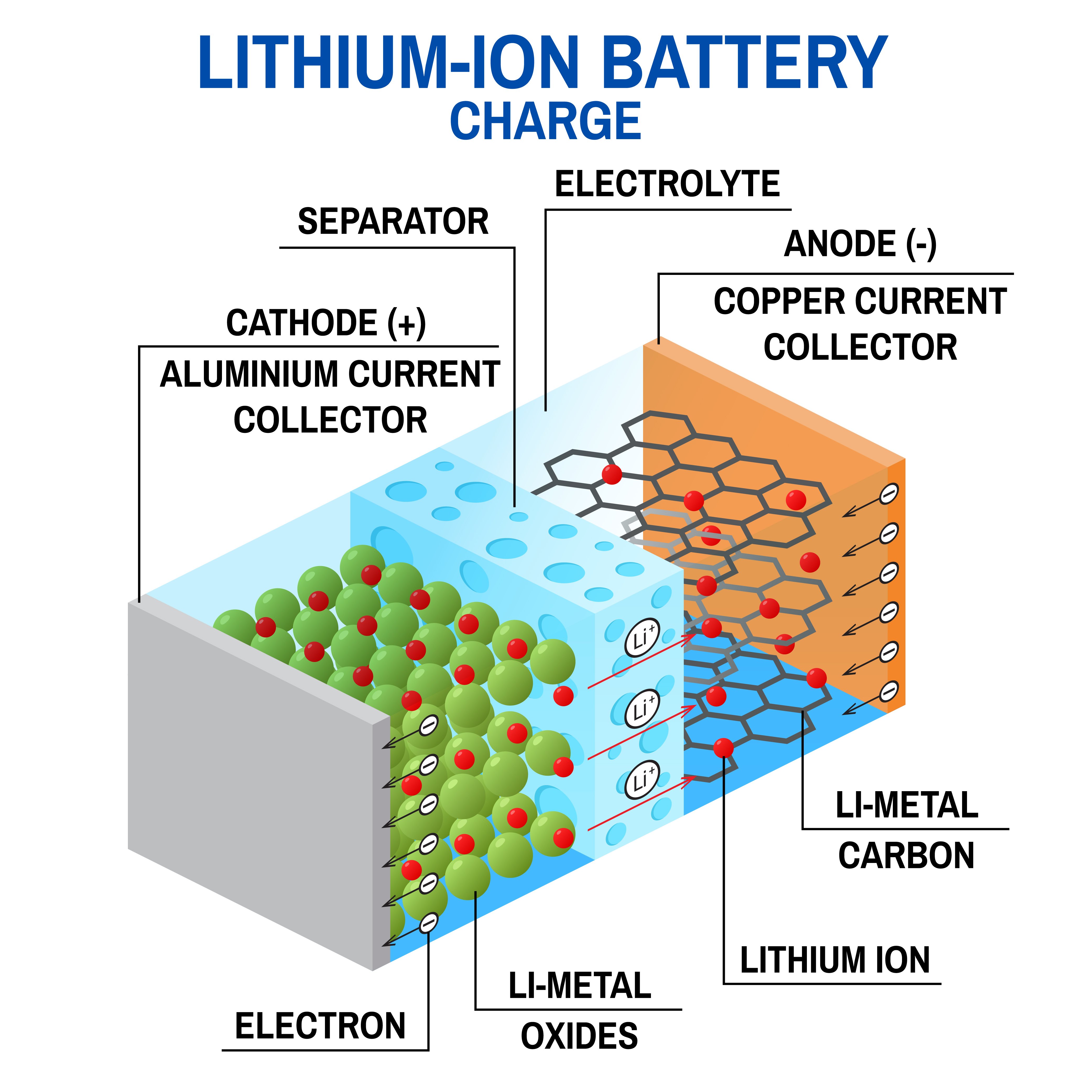
The electric scooter lithium-ion battery comprises a series of interconnected 18650 or 21700 electrochemical cells stacked together to form a battery module. Essentially, these li-ion cells work like any electrochemical cell - generating electrical energy via chemical reactions that ultimately provide power to your electric scooter.
Each battery cell contains three or four essential components: a cathode, anode, electrolyte, and separator.
- Cathode: the positive electrode, which is made up of lithium metal oxides, e.g., lithium-cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), and generates the lithium ions and electrons used in the electrochemical process
- Anode: the negative electrode, which is mainly made up of layers of loosely bonded graphite or lithium-carbon compound and offers a surface for intercalation for the Lithium ions and electrons produced by the anode.
- Electrolyte: It is usually a lithium-based salt electrolyte housed in an organic solvent that helps transport the lithium ions from the cathode to the anode and vice versa.
- Porous Separator. Located between the anode and cathode, it acts as the safety barrier that prevents the content of the cathode and anode from mixing while selectively allowing only lithium ions to pass through it.
In simple terms, a lithium battery works by allowing lithium ions to travel back and forth between the terminals via the separator while also allowing electrons to freely move to and from the terminals through an external circuit. This two-way movement of ions and electrons creates the electrical energy that powers your electric scooter and also facilitates charging.
Let's now dive into the intricate process that occurs during charging and discharging, as the processes involved are not the same.
What Happens When a Scooter Lithium-Ion Battery Is Charged?
During the charging of lithium ion cells, electrons are attracted and removed from the lithium in the lithium metal oxide (cathode) by the positive side of the power source. These electrons then flow through the external circuit to the anode, as they cannot flow through the separator; at the same time, the free positive lithium ions formed are attracted towards the negatively charged terminal and will use the shorter route via the separator. Upon reaching the graphite layer, they combine to form lithiated carbon (LiC6).
When all of the lithium ions have moved to the anode, the battery is said to be fully charged. However, this is an unstable state, and as soon as the power source is removed, the lithium ions will want to return to their more stable state as part of the metal oxide in the cathode.
What Occurs During Lithium Ion Battery Use/Discharge
After removing the power source, the lithium ions will migrate back to the cathode (which offers a much more stable state) via the separator. The electrons will also flow back to the cathode, but again via an external circuit, i.e., the device it’s powering. The flow of electrons and ions back to the cathode is what produces the electrical energy required to power the scooter. When all lithium ions and electrons have returned to the cathode and re-formed the lithium metal oxide, the e-scooter battery is considered drained and in need of recharging.
Now that we know how lithium-ion batteries work, let's take a deeper look at what could cause them to catch fire and the common causes behind these incidents.
Why do Electric Scooter Batteries Catch Fire?
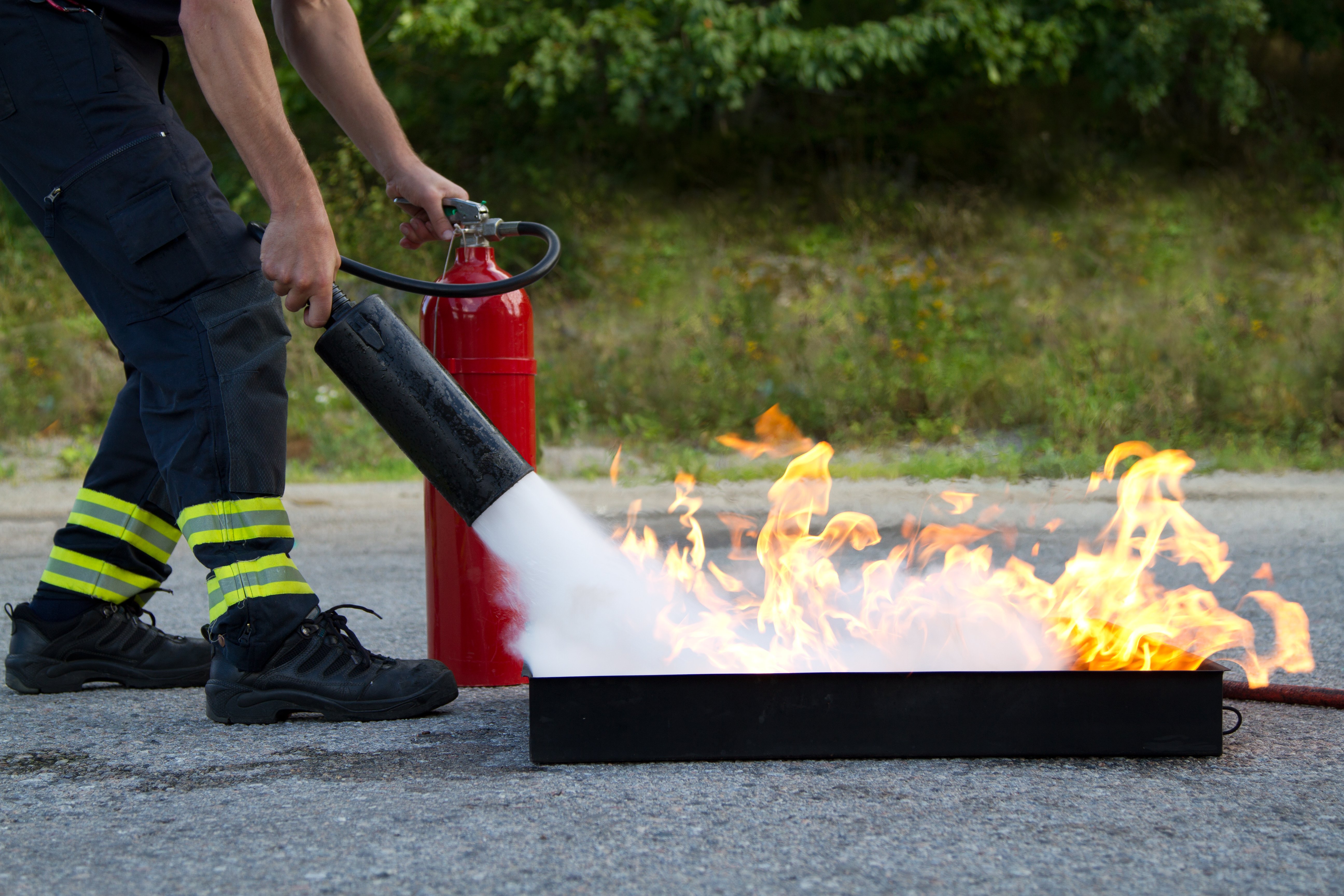

As we have seen, batteries generate electrical energy through chemical processes. For it to be safe, it needs to be done in a controlled environment under the stated optimum conditions. If these ideal conditions are disrupted due to a flaw of any kind, be it an internal or external failure, it can lead to dangerous reactions, short circuits, and even potential fire and explosions.
So what can make a battery not work as it's intended to? The key culprits are:
Manufacturer Defects.
These defects include faulty wiring and circuits, design flaws, poor soldering, and low-quality components. All of these flaws might cause battery failure and finally result in the battery igniting and catching fire.
Avoid using poor quality or counterfeit batteries in your electric scooter. These batteries are often made with defective materials that can easily catch fire if they overheat. Additionally, these batteries may not have proper safety features and battery management systems that can detect if a battery is operating beyond its limits, thereby preventing the events leading to a possible fire.
Battery Abuse
Battery abuse can take the form of :
Mechanical Abuse
This includes anything that disfigures the structure of the battery, such as dropping, piercing, crushing the battery, and exposing it to harsh conditions. Mechanical abuse can lead to the deformation of the li-ion cell and the separator, which may in turn cause an internal cell short circuit
If an electric scooter falls or is involved in a collision, it can damage the battery, so always inspect your scooter afterward and take it to a qualified technician if there are any concerns about the integrity of the e scooter battery.
Electrical Abuse
Involves overcharging or over-discharging the battery. This leads to the formation of dendrites, electrolyte decomposition, and metal dissolution, which are all recipes for short circuits within the cell. This process can also emit gasses like Oxygen, Hydrogen, and Carbon monoxide.
To avoid electrical abuse, riders should never attempt to:
- Tamper with their electric scooter's internal circuitry, electrical system or wiring.
- Attempt to modify their e-scooters with aftermarket parts not designed for use with their particular model. In these cases, the parts may not be compatible with the battery, or they can put too much strain on it, leading to a fire.
- Charge the battery with the wrong charger
Thermal abuse
Occurs when the battery is exposed to extremely high temperatures, such as direct sunlight, that lead to the separator collapsing again, leading to an internal short circuit.
Eventually, all these processes result in a rapid chain reaction known as thermal runaway and propagation. This phenomenon accelerates the rate and severity of unwanted reactions, leading to further escalation.
So What is Thermal Runaway?
Thermal runaway occurs when the materials in the battery decompose exothermically-meaning they release heat. The heat generated by this process exceeds the amount of heat that is dissipated into its surroundings.
The result is an uncontrollable, self-heating state where chemical reactions are exponentially accelerated and internal temperatures continue to rise.
If nothing is done to counter this process, then the battery will continue to overheat rapidly, possibly leading to what is known as "thermal runaway propagation," meaning that the energy released from a single battery will begin to affect other batteries in close proximity. This results in an ever-accelerating chain reaction of increased temperatures, excessive heat and pressure, potentially leading to catastrophic consequences such as fires, toxic smoke, or explosions if not contained quickly.
This process is even more lethal because the fire is self-sustaining and has all three components required for combustion: fuel (in the form of combustible electrolytes present in the battery), heat, and oxygen, which are created as byproducts of the undesirable chemical reactions.
As you can see, lithium-ion battery fires can have serious consequences if left unchecked, so it's important to take all proper precautions when using them. If you believe your electric scooter is at risk of a battery fire, seek the help of a qualified technician immediately. Additionally, if you are ever in the vicinity of an e scooter fire, get away from it and call emergency services immediately.

Are Electric Scooter Lithium-ion Battery Fires That Common?
Electric scooter batteries have come under fire recently, literally and figuratively, and as an avid e-scooter enthusiast, this is obviously worrying to hear. However, it is important to consider that one video of a fire can be shared multiple times over the internet and make it seem like these occurrences are a lot more commonplace than they actually are. In reality, they are very rare and easily preventable with a few simple safety precautions.
So while it pays to bear the potential fire risks in mind, don't worry unnecessarily. Get out there and enjoy your e-scooter ride—just be sure to practice the safe habits we have discussed.
Stay current with the latest U.S. electric scooter laws in our 2025 guide. Updated annually since our first comprehensive guide, ensuring you have the most recent state and city regulations to ride responsibly”

The Slack Core 920R is currently the fastest electric scooter in 2025 that you can purchase without the need for pre-order.

Our selection of the best electric scooters 2025 spans the fastest e-scooters to the most portable ones, the ones designed for city riding and off-road, the best scooters for rain, budget electric scooters for students, and more powerful ones for skilled riders.
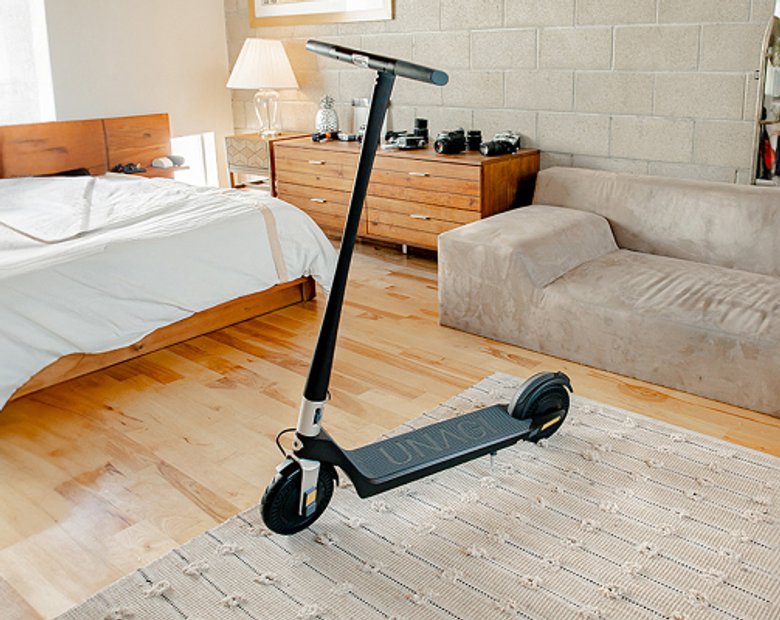

The Unagi Voyager is the best lightweight electric scooter for adults and teenagers. It is the ultraportable sequel to its predecessor, the Unagi Model One Classic.
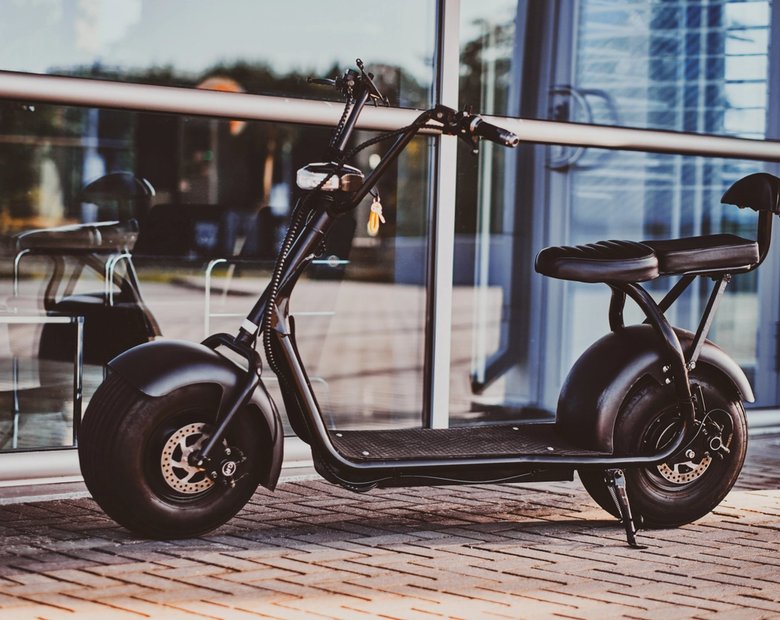

If you're wondering whether an electric scooter with a seat is right for you, this is a detailed article that would suit your need.
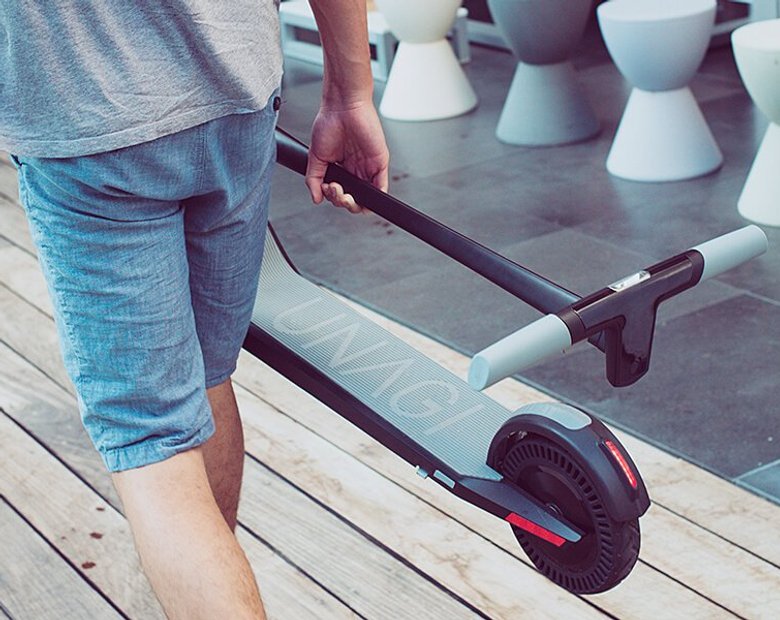

Understand which personal electric vehicle is best, the choice between an electric bike or electric scooter might already be made for you by some critical factors, including portability and storage capacity.
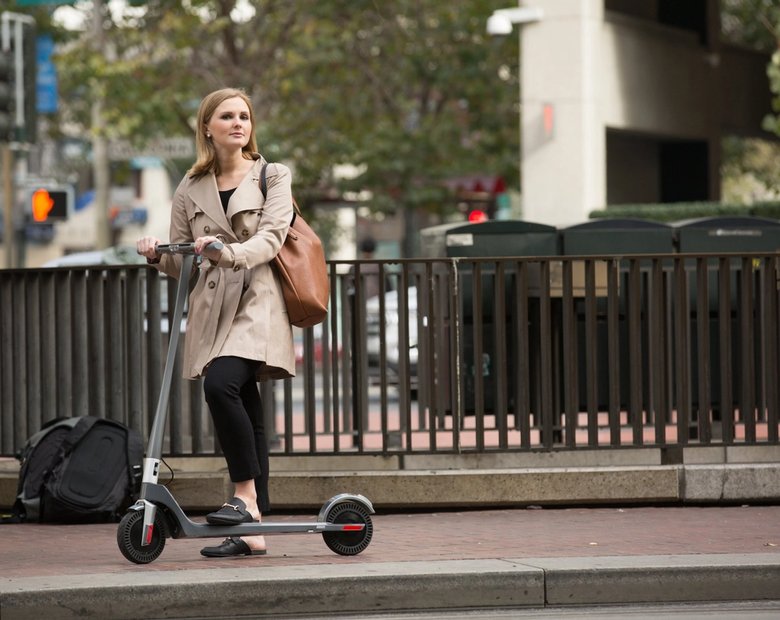

In the U.S., most states don't require a license. For those that do, they usually just ask for a regular driver's license or a learner's permit.

Yes, you can bring an electric scooter on a plane, but it needs to have a lithium battery smaller than 100 watt-hours, which most don't.

Manufacturers advise against riding electric scooters in the rain. The main reasons are: water can fry the electronics, make the ride dangerous, and void your warranty.

The basis and the premise of my work is that we either operate out of love or we operate out of fear...Time is currency. The coolest thing about the scooters is that it's really quick, and it goes uphill. From there, traveling more efficiently and having a good time doing it--I think that's the most important thing.

Cynthia Leu has a full plate. A tech worker by day, Cynthia spends her off time balancing the parallel lives of a powerlifter, entrepreneur, mental health advocate, and more. Riding Unagi helps this USMC veteran cut down on everyday…

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7m2hVBE62LY Rasheed Muhammad is sick of Los Angeles traffic. In order to preserve his sanity, Rasheed has traded his everyday driving habit for the portable and beautiful Unagi Model One. It’s an essential accessory for navigating LA streets -- and…

Rich Lee, Co-Founder of San Francisco’s SPRO Coffee Lab, wants to share his love for coffee with the world. He depends on riding Unagi to avoid the hassle of navigating the parking crunch in the booming Mission Bay neighborhood.…